The key to comprehensive infection prevention and control planning is to do well in epidemic prevention and control and purify the patient care area.
In the laboratory research, pulsed high-intensity light technology has been proved to be effective in disinfection and sterilization. In order to further study the environmental efficiency and feasibility of this non-contact technology, a professional Research Institute conducted a four-month study at Queen’s Hospital in North London, UK.
This study was carried out from July 2014 to November 2014. 40 isolation wards in the hospital were selected as the study samples. After the patients were discharged from the hospital, they were cleaned manually with hypochlorite solution, and finally sterilized with pulse ultraviolet disinfection equipment. After that, professionals took samples of aerobic bacteria, exposed the inoculated agar plate to non patient care area, and tested pulse ultraviolet disinfection. The effect of the equipment on the microorganism will also record the hospital staff’s feelings on the use of the equipment.
Experimental method
The research team designed a comparative study to sample five high-frequency contact surfaces (bed railings, pallet tables, bathroom handrails, toilet seats and bathroom faucet handles) before disinfection, after artificial disinfection and after disinfection of pulsed ultraviolet disinfection equipment to evaluate the effectiveness of pulsed ultraviolet disinfection equipment in on reducing environmental pollution in isolation wards of discharged patients’ gender.
Sample selection
Select wards (6 rooms per unit) from acute medical assessment units. The laboratory is determined by the database of infection prevention and control for the use of infection prevention and control personnel. The selection criteria of the laboratory are as follows:
(1) Must be a single room;
(2) Must stay at least 48 hours;
(3) Must be removed on the same day of sample collection;
(4) Must be used as a contact isolation chamber.
Experimental process
Baseline microbiological samples were collected after discharge, but prior to standard regular cleaning. Five high frequency contact surfaces were first sampled by trypsin soybean agar contact plate (Oxford, Basingstoke, UK) with a diameter of 5 mm;
Hospital cleaners use 1000 ppm (0.1%) chlorine disinfectant (activalum Plus; Ecolab, Cheshire, UK) for standard terminal cleaning and second sampling;
The room was irradiated by a pulse disinfecting robot. Three points were selected for each ward: two sides of the bed and the bathroom. Each point was irradiated for 5min. After disinfection, samples were collected from the same 5 surfaces to complete the final sampling.
The collected sample is placed on a pre selected surface to prevent any deviation or change of cleaning method. After sample collection, trypsin soybean agar contact plate returned to the laboratory, cultured in air at 37 °C for 48 hours, counted and recorded the number of colony forming units (CFU).
Data analysis
One room was rejected because there was no information about infection of pulse equipment, and the sample was reduced to 39 rooms.
At baseline, the largest proportion (93%) of the contaminated rooms was observed on the surface of the bed railings, which was reduced to 36% after manual cleaning and 7% after disinfection by the pulsed ultraviolet disinfection robot.
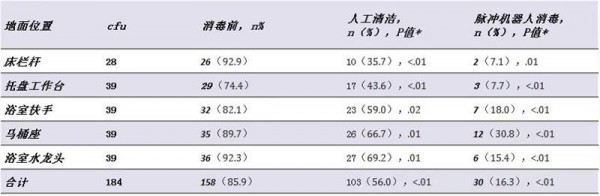
Experimental result
After the robot was sterilized by pulsed UV, the bacterial contamination in CFU decreased by 78.4%, 91% lower than the initial bioburden level. The CFU of MDROs on the nail plate was reduced by 5 log. Through investigation and research, the equipment operators are satisfied with the comfort of the product.
Conclusion
More and more innovative non-contact disinfection equipment is used in the whole medical field to ensure the cleanness of hospital environment. Through this experiment, we found that:
1. The combination of artificial cleaning and chemical disinfection failed to effectively remove the microbial pollution in the environment.
2. After using pulse ultraviolet disinfection equipment, the surface pollution of isolation ward was significantly reduced.
Media Contact
Company Name: Shenzhen Doneax Science and Technology CO., LTD
Email: Send Email
Phone: 0086 18013988586
Country: China
Website: https://www.doneaxmedical.com/

