Quenching cracks are common quenching defects in CNC machining, and there are many reasons for them. Because heat treatment defects start from product design, Anebon believes that the work of preventing cracks should start from product design. It is necessary to correctly select materials, reasonably carry out structural design, put forward appropriate heat treatment technical requirements, properly arrange process routes, and choose reasonable heating temperature, holding time, heating medium, cooling medium, cooling method and operation mode, etc.

1. Materials
1.1 Carbon is an important factor affecting the tendency of quenching and cracking. The carbon content increases, the MS point decreases, and the quenching crack tendency increases. Therefore, under the condition of satisfying the basic properties such as hardness and strength, the lower carbon content should be selected as far as possible to ensure that it is not easy to quench and crack.
1.2 The influence of alloying elements on quenching cracking tendency is mainly reflected in the influence on hardenability, MS point, grain size growth tendency and decarburization. Alloying elements affect the quenching cracking tendency through the influence on hardenability. Generally speaking, the hardenability increases and the hardenability increases, but at the same time as the hardenability increases, it is possible to use a quenching medium with weak cooling capacity to reduce quenching deformation to prevent deformation and cracking of complex parts. Therefore, for parts with complex shapes, in order to avoid quenching cracks, it is a better solution to choose steel with good hardenability and use a quenching medium with weak cooling capacity.
Alloying elements have a great influence on the MS point. Generally speaking, the lower the MS, the greater the quenching crack tendency. When the MS point is high, the martensite formed by the phase transformation may be self-tempered immediately, thereby eliminating part of the phase transformation. Stress can avoid quench cracking. Therefore, when the carbon content is determined, a small amount of alloying elements should be selected, or steel grades containing elements that have little effect on the MS point.
1.3 When selecting steel materials, overheating sensitivity should be considered. Steel that is sensitive to overheating is prone to cracks, so attention should be paid to the selection of materials.
2. Structural design of parts
2.1 The section size is uniform. Parts with a sharp change in cross-sectional size will have cracks due to internal stress during heat treatment. Therefore, the sudden change of section size should be avoided as far as possible during design. The wall thickness should be uniform. If necessary, holes can be drilled in thick-walled parts that are not directly related to the application. Holes should be made as through holes as possible. For cnc machining aluminum parts with different thickness, separate design can be carried out, and then assembled after heat treatment.
2.2 Round corner transition. When the parts have corners, sharp corners, grooves and horizontal holes, these parts are prone to stress concentration, which will lead to quenching and cracking of the parts. For this reason, the parts should be designed in a shape that does not cause stress concentration as much as possible, and the sharp corners and steps are processed into rounded corners.
2.3 Difference in cooling rate due to shape factor. The speed of cooling varies with the shape of the parts when the parts are quenched. Even in different cnc parts of the same part, the cooling rate will be different due to various factors. Therefore, try to avoid excessive cooling differences to prevent quenching cracks.
3. Technical conditions of heat treatment
3.1 Local quenching or surface hardening should be used as much as possible.
3.2 Reasonably adjust the local hardness of the quenched parts according to the service conditions of the parts. When the local quenching hardness requirement is low, try not to force the overall hardness to be consistent.
3.3 Pay attention to the mass effect of steel.
3.4 Avoid tempering in the first type of tempering brittle zone.
4. Reasonably arrange the process route and process parameters
Once the material, structure and technical conditions of the steel parts are determined, the heat treatment technicians must conduct process analysis to determine a reasonable process route, that is, to correctly arrange the positions of preparatory heat treatment, cold processing and hot processing and determine the heating parameters.
Quenching crack
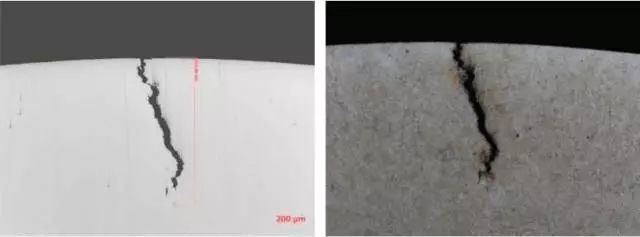
4.1 Under 500X, it is jagged, the crack at the beginning is wide, and the crack at the end is small to none.
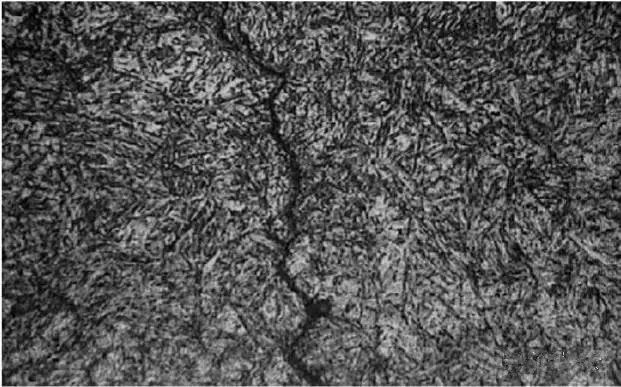
4.2 Microscopic analysis: abnormal metallurgical inclusions, cracks extending in a jagged shape; observed after corrosion with 4% nitric acid alcohol, there is no decarburization phenomenon, and the microscopic appearance is shown in the figure below:
1# sample
No abnormal metallurgical inclusions and decarburization were found at the cracks of the product, and the cracks extended in a zigzag shape, which has the typical characteristics of quenching cracks.

2# sample
Analysis conclusion:
4.1.1 The composition of the sample meets the requirements of the standard and corresponds to the composition of the original furnace number.
4.1.2 According to microscopic analysis, no abnormal metallurgical inclusions were found at the cracks of the sample, and there was no decarburization phenomenon. The cracks extended in a zigzag shape, which has the typical characteristics of quenching cracks.
forging crack
1. Cracks caused by typical material reasons, the edges are oxides.
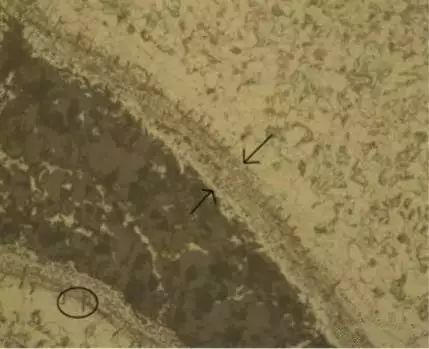
2. Micro observation
The bright white layer on the surface should be the secondary quenching layer, and the dark black under the secondary quenching layer is the high temperature tempering layer
Analysis conclusion:
Cracks with decarburization should be distinguished whether they are raw material cracks. Generally, the cracks with decarburization depth greater than or equal to the surface decarburization depth are raw material cracks, and the cracks with decarburization depth less than the surface decarburization depth are forging cracks.
With Anebon’s leading technology likewise as our spirit of innovation,mutual cooperation, benefits and development, we’re going to build a prosperous future together with your esteemed enterprise for OEM Manufacturer Custom High Precision aluminum parts, turning metal parts, cnc milling steel parts, And there are also a lot of overseas close friends who came for sight seeing, or entrust us to buy other stuff for them. You will be most welcome to come to China, to Anebon’s city and to Anebon’s manufacturing facility!
China Wholesale China machined components,cnc products, steel turned parts and stamping copper. Anebon has advanced production technology, and pursuit innovative in products. At the same time, the good service has enhanced the good reputation. Anebon believe that as long as you understand our product, you must be willing to become partners with us. Looking forward to your inquiry.
Media Contact
Company Name: Anebon Metal Products Co., LTD.
Contact Person: Media Relations
Email: Send Email
Phone: +86-13509836707
Country: China
Website: https://www.anebon.com/


