Just like a car needs fuel to run, the liver requires its own form of “fuel” to maintain optimal functioning. Besides maintaining a balanced diet, it is essential to supplement with nutrients that support liver health.
Therefore, the nutritional components for liver maintenance and protection have naturally become a focal point in the field of nutritional supplements. Addressing the current focus on liver health, ESTHELIV LAB, from the perspective of nutritional intervention, has identified a combination of ingredients, namely PQQ and inositol, that deeply stabilize liver cells and enhance liver function. Next, exploring the effectiveness of this liver-protective formula from three perspectives.
I. How are PQQ and Inositol Different from Other Liver-Protective Ingredients on the Market?
Differing from other liver-protective ingredients on the market, PQQ and inositol have gained attention through their efficacy. They fall under a category known as cellular coenzyme ingredients. The advantage of these ingredients lies in being a general term for a large class of organic auxiliary factors naturally present and necessary in the human body. Unlike many plant-extracted components commonly found on the market, coenzymes are naturally occurring and essential nutritional elements in the human body.
Most biochemical reactions in the body, including synthesis, metabolism, detoxification, and defense, occur in the liver. Coenzymes have been proven to activate cellular nutrition and cellular energy, enhancing the immune system, boosting antioxidant capabilities, delaying aging, increasing vitality, and providing liver protection. As a result, the liver naturally requires more coenzymes to participate in energy metabolism and conversion.
However, with age, the body’s ability to self-synthesize coenzymes within the liver gradually decreases. At this point, external supplementation of coenzymes becomes essential. PQQ and inositol, being naturally present in the body and directly acting on liver cells, stand out as liver-protective components.
II. How Do These Two Cellular Coenzyme Components Protect the Liver?
PQQ:
PQQ has gained attention for its anti-aging effects, but its liver-protective effects are equally significant. The core function of PQQ in liver protection lies in enhancing the power of liver cells as cellular generators. Mitochondria, as the energy core of cells, provides 95% of the body’s required energy, including liver cells. PQQ not only repairs damaged liver cells and generates fresh, healthy cell mitochondria but also stimulates mitochondrial activity, strengthening mitochondrial function.
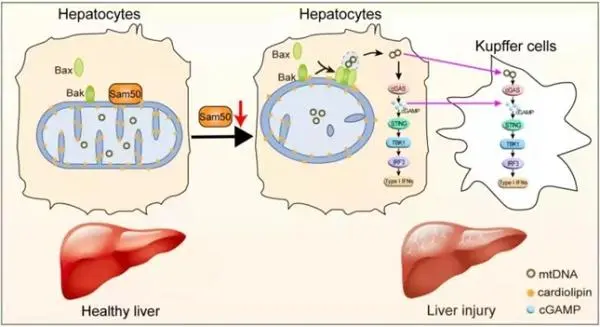
When mitochondrial function improves, liver cells have enough power to metabolize excess fat, waste, and toxins, reducing the damage caused by these substances to the liver. Additionally, PQQ has been shown to participate in the metabolism of ethanol, reducing serum bilirubin, alanine transaminase, and lactate dehydrogenase levels, and inhibiting hepatic lipid peroxidation, providing a clear detoxification and liver-protective effect.
Given that the liver is the main organ for ethanol metabolism, especially after alcohol consumption, the ability to quickly metabolize ethanol and acetaldehyde is crucial in preventing alcohol-induced liver damage. A study published in the journal Process Biochemistry in 2020, using a mouse model, confirmed that the administration of PQQ significantly increased the levels of ethanol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase in liver tissue, supporting the idea that PQQ accelerates ethanol metabolism and potentially protects against alcohol-induced liver damage.
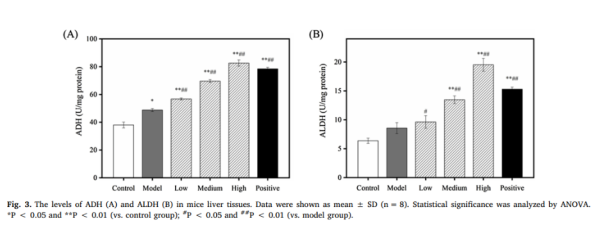
Inositol:
Inositol plays a role in transmitting signals and supplying nutrients within cells. It is involved in various physiological processes, such as aiding in liver emulsification and metabolizing fats. Inositol is also known as the “anti-fatty liver vitamin.” By accelerating the metabolism of fat in the body, it facilitates the emulsification and elimination of excess fat from the liver. Additionally, inositol regulates fat metabolism, helping the liver optimize surplus fat and reduce the likelihood of developing fatty liver.
Inositol also has a regulatory effect on insulin resistance. Studies suggest that insulin resistance may be one of the factors leading to fatty liver, as it can cause an increase in insulin levels in the body, prompting the liver to synthesize and store more fat. Moreover, insulin resistance may affect the metabolism of fat, making it easier for fat to accumulate in the liver, potentially leading to the development of fatty liver.
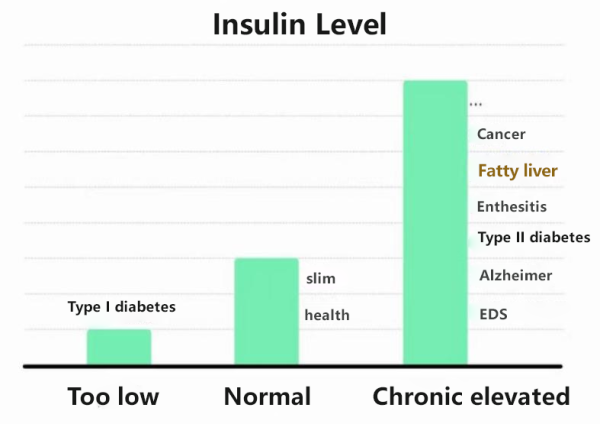
Inositol can enhance signal transduction by activating IPGs, strengthening the insulin pathway. This translates into promoting glucose uptake and utilization, inhibiting fatty acid synthesis, promoting fatty acid oxidation, and reducing the risk factors for fat degeneration at the source, defending against the occurrence of metabolic imbalances.
III. Does the Combination of PQQ and Inositol Have Better Effects?
The answer is affirmative. The combination of PQQ and inositol synergistically protects the liver in multiple dimensions.
Synergistic Optimization of Energy Metabolism:
Inositol enhances the insulin pathway, promoting glucose utilization and preventing the risk of problems such as fatty liver caused by metabolic imbalance at the source. On the other hand, PQQ, through mitochondrial regulation, optimizes the state of liver cells, thereby enhancing cellular energy production and optimizing energy conversion efficiency. Together, they synergize to optimize the energy status of liver cells, contributing to the stability of liver output.
Synergistic Antioxidant Defense Against Liver Damage:
Besides optimizing energy metabolism to prevent issues like fat accumulation and alcoholic fatty liver, both inositol and PQQ have a clear protective effect against oxidative stress produced during cellular metabolism.
Sustained inflammation is the final link to liver damage and the continuous development of fatty liver. Oxidative stress leads to the accumulation of oxidants within cells, damaging the structure and function of liver cells. Both inositol and PQQ have distinct protective effects in terms of oxidative stress generated during cellular metabolism.
In summary, the combination of PQQ and inositol has shown to have a synergistic and comprehensive protective effect on the liver. From optimizing energy metabolism to defending against oxidative stress, these two substances work together to maintain liver health and immune balance.
Therefore, PQQ and Inositol’s liver protection formula is of great concern is not empty talk. ESTHELIV Liver Detox Capsules also adheres to the principle of effective formulations, with dedicated research and development, scientific proportioning, and a strong combination of cellular ingredients for deep liver protection and liver cleansing, to strengthen the health of the liver from the source.
Reference:
[1] Liang, C., et al., A subchronic oral toxicity study on pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) disodium salt in rats. (1873-6351 (Electronic)).
[2] F. S. Faccini, N. Hua, F. Abbasi, and G. M. Reaven, “Insulin Resistance as a Predictor of Age-Related Diseases,” Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 86, no. 8 (2001): 3574–78.
Media Contact
Company Name: ESTHELIV,INC
Contact Person: Becko
Email: Send Email
Country: United States
Website: www.estheliv.com
